OMEGA-3 FOR FERTILITY
Most of us have heard of Omega-3 being great for heart health and lowering cholesterol but what about Omega-3 for fertility?
Studies show that adequate amounts of Omega-3 are beneficial for a range of health conditions, including improving fertility (both natural conception and IVF) as it can reduce oxidative stress to reproductive organs and therefore minimize damage to eggs (Lass A, Balluzzi A. 2019). Not to mention oxidative stress is the number one leading factor when it comes to egg health so we want to do everything we can to reduce oxidative stress.

SO, WHAT ARE OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS?
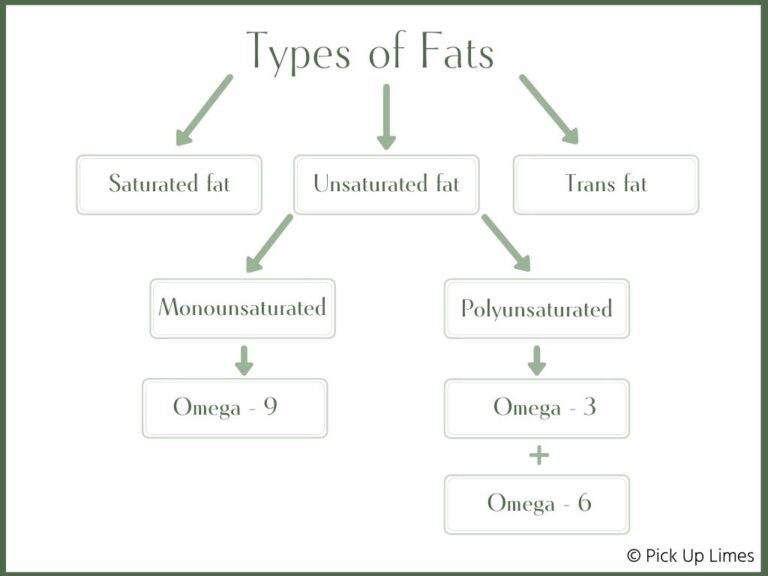
Let’s break this down in simple terms. Dietary fats can be categorized into three types: trans fat, saturated fat, and unsaturated fat. Unsaturated fat is liquid at room temperature and considered ‘beneficial fats’. Unsaturated fats are further broken down into monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Omega-3 and omega-6 are both polyunsaturated fats.
Within the category of omega-3 there are three main types:
- Alpha-linolenic Acid (ALA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
ALA is found in plant oils, EPA and DHA are both found in fish oils.
REDUCING OMEGA-6 INTAKE
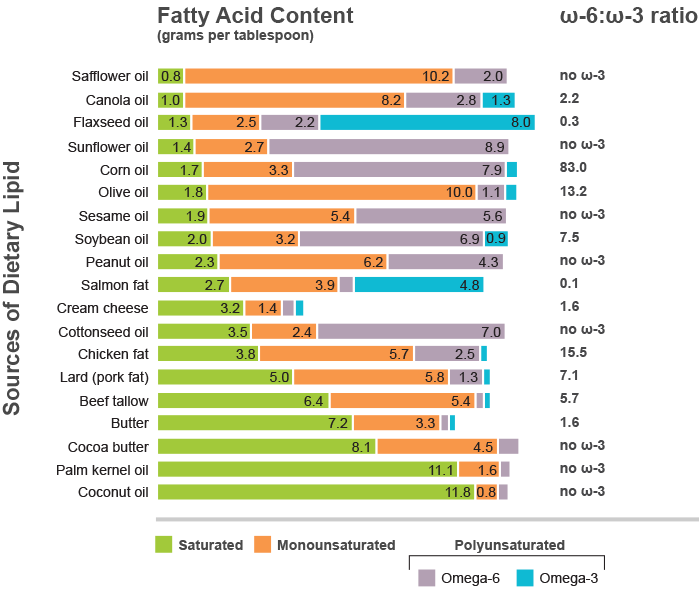
Omega-6 is a major proinflammatory factor in the body while omega-3 is anti-inflammatory (Esther Tortosa-Caparros, 2017). It is important to know that ALA and omega-6 use the same metabolic pathway in the body. Therefore they are competing with each other and most times omega-6 will be metabolized over ALA. As a result, omega-6 sources need to be reduced in the diet and omega-3 sources need to be increased in order to optimize absorption.
Many sources of omega-3 also contain omega-6, it’s important to be aware of the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio of foods.
Some Omega-6 Sources Include:
- Corn
- Soybean Oil
- Peanut Oils
- Sesame Oil
- Baked goods
- Safflower & Sunflower oils
Once omega-3s are in the preferred form, the body utilizes the fatty acids to help combat inflammation, works to reduce clotting and has also been shown to protective against cardiac arrhythmia
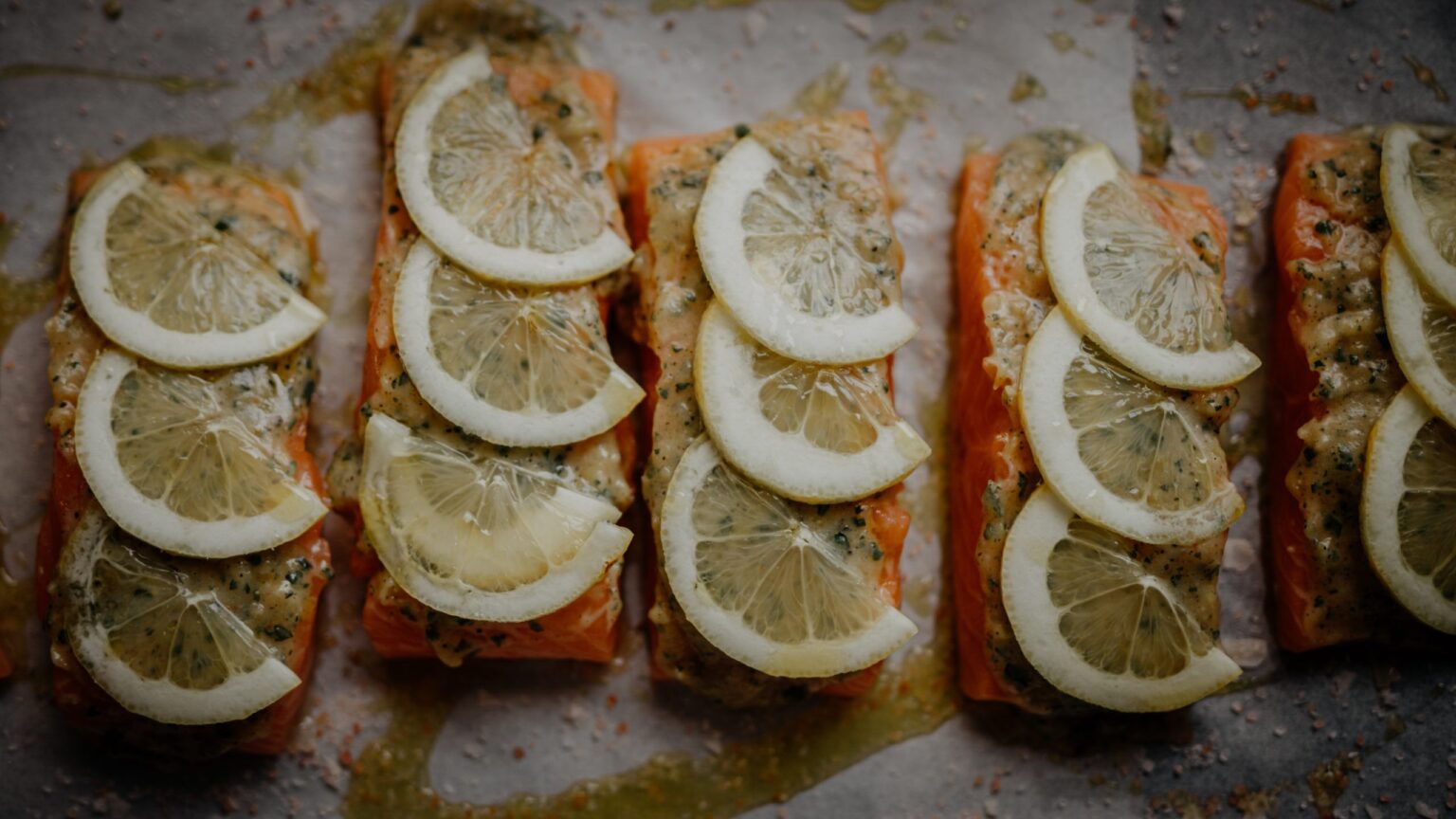
FOOD SOURCES OF OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS
ALA is found primarily in plants. If you are a vegetarian or vegan, you want to be including these daily and consider an omega-3 supplement
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Legumes
- Pumpkin seeds
- Flaxseed oil
- Soybeans
- Tofu & other soy products
EPA & DHA (or the long-chain omega-3 fats) are primarily found in marine sources:
- Salmon
- Canned Tuna
- Trout
- Sardines
- Mackerel
- Herring
- Cod Liver Oil
- Anchovies
- Caviar
- Oysters
Individuals should be encouraged to consume a 5.3 oz serving (150g) of fish 2 – 3 times a week (300 – 350g) if possible, at least three months prior to fertility treatments or conception as this is the time it takes for immature egg maturation.
The types of fish to avoid due to their higher levels of mercury include:
- Orange roughy (sea perch)
- Catfish
- Shark (flake)
- Swordfish
- Marlin
Seek advice from an Accredited Fertility Dietitian to review your omega-3 intake and how it can be improved before considering supplementation.

HOW DOES OMEGA-3 IMPROVE FERTILITY
It has been concluded through numerous studies that couples who eat fish at least twice a week have a higher chance of falling pregnant than those who ate fish less frequently.
A recent US study analyzing over 500 couples who were trying to conceive found that couples who consumed at least eight servings of seafood per cycle, fertility was 61% higher compared to couples that consumed less than one serving of seafood per cycle (Gaskins, et al., 2018). Specifically, 92% of couples who consumed at least two servings of seafood per week were pregnant by 12 months in the study versus 79% among couples consuming less.
Another recent study of one hundred women undergoing Assisted Reproductive Therapy found that women who had a higher intake of omega-3 in their diet, had higher rates of implantation than those who consumed less omega-3 (Chiu YH, 2018). Although, research seems to suggest that it’s not just omega 3 that’s helpful… replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats seems to be beneficial for implantation in general (Eskew AM, 2017).
The findings of another recent study of 900 women between the ages of 30-44 years trying to conceive in <3 months, showed that the odds of conceiving are one-and-a-half times greater among women who supplement their diet with omega-3 than those who did not (J.Stanhiser, 2022). The study was not dose specific and all participants had regular periods with no history of smoking. The results showed women taking omega-3 supplements were significantly more likely to conceive (n = 96 out of 113, or 84.96%) vs those not using them (n = 409 out of 787, or 51.97%; P<0.001). Omega-3 supplement intake on at least 20% of menstrual cycle days was associated with approximately twice the probability of conception.
HOW MUCH OMEGA-3 IS ‘ENOUGH’?
‘Enough’ is certainly determined person-to-person.
The National Institutes of Health suggests consuming 1.1-1.6 grams of omega-3 a day. In reference, it takes about 4-5 ounces of Atlantic salmon to provide 3 grams of omega-3. Fish oil supplements typically provide 300 mg per pill, though doses vary.
The American Pregnancy Association recommends:
- 300 mg DHA daily for pregnant & breastfeeding women
- 500 mg EPA & DHA for all adults
The World Association of Perinatal Medicine Dietary Guidelines recommends at least 200mg DHA and/or EPA Omega 3 fats each day before and during pregnancy, which equates to two oily fish meals per week.

WHAT ABOUT FISH OIL SUPPLEMENTS?
Fish oil supplements are one of the most commonly used nonvitamin/mineral dietary supplements by the U.S adults (T.Clarke, 2015). Data from the 2012 National Health Interview Survey indicate that 7.8% of U.S. adults and 1.1% of U.S. children use supplements containing fish oil, omega-3s, and/or DHA or EPA.
Though it is best to get your omega-3 from food, sometimes that is not always possible. Whether you have a fish allergy or you just don’t like the taste, it could be really useful to take a fish oil supplement to ensure that you are getting the recommended amount.
Fish oil doses vary depending on the person and the goal of supplementation. For general health, 250mg of combined EPA and DHA is the minimum dose.
Choosing the right fish oil supplement:
- It is important to choose a fish oil supplement that is manufactured with quality standards.
- Be sure the company is transparent about the quality of their fish oil regarding mercury content.
- Make sure that the fish oil is not smelly. Research shows that fish oils only smell unpleasant when the oil has started to degrade and is becoming rancid.
- Make sure that the fish oil does not taste fishy. The freshest and highest-quality fish oils should not taste fishy. Avoid fish oils that have really strong or artificial flavors added to them because they are most likely trying to hide the fishy flavor of rancid oil.
Consult your dietitian before starting any kind of supplementation for correct dosages and kind.
Want to know whether your diet and supplement regime are meeting all your omega-3 needs for fertility?
Radically Rooted offers omega-3 testing so you know how much omega-3s are in your red blood cells! We can then implement a personalized plan to boost your numbers and re-test in 4-6 months! Get in touch today for more information.

Looking for a dietitian to help boost your omega-3 status and learn more about the role of food in your fertility journey?



