How Weight Affects Fertility in Women
Does body weight impact the ability of women to get pregnant? Great question. According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), 6% of women who have never been pregnant have fertility issues due to obesity. The most effective way to improve your fertility is by achieving a healthy weight.
Research shows being underweight (BMI <18.5) can reduce a woman’s fertility by causing hormone imbalances that affect ovulation, implantation and overall chance of getting pregnant. On the other hand, being overweight (BMI of 25-29.9) or obese (BMI over 30) can also affect fertility in women. Excess weight in women can lead to hormonal imbalances, ovulation problems, and menstrual disorders, which reduce the chances of conceiving. It can also lead to difficulties with assisted reproduction, such as in-vitro fertilization (IVF), ovulation induction, and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Let’s dig a little bit deeper into HOW a woman’s weight affects fertility…
How Weight Affects Fertility During Ovulation
Excess body fat is one of the most common causes of ovulatory dysfunction. The ovaries create the female hormone estrogen. The ovaries produce the female hormone estrogen, but fat cells also produce estrogen. As body fat increases, fat cells release more estrogen, leading to hyperestrogenism.
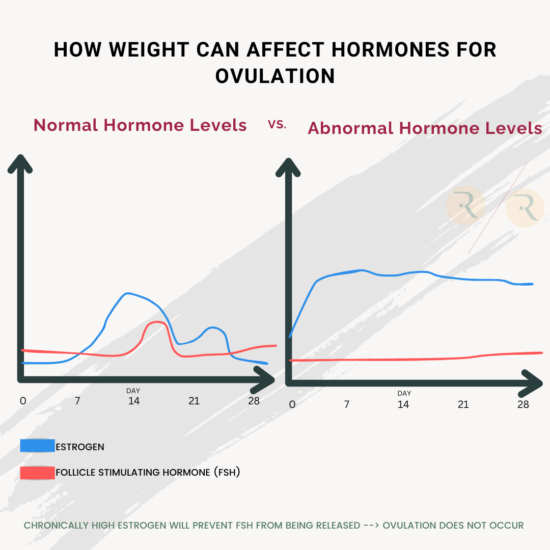
In a healthy menstrual cycle, estrogen levels are at their lowest during the 1-7 days leading up to ovulation. The low level of estrogen signals the brain to produce follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to stimulate the maturation of the eggs for ovulation. If a woman’s estrogen is chronically high as seen with hyperestrogenism, it prevents the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and/or luteinizing hormone (LH). This weakens the signal for the body to start maturing eggs thereby affecting the ability to ovulate. These hormones are necessary for ovulation which is why it is a problem when they are out of balance. As such, women who are overweight or obese are up to three times more likely to experience irregular periods and less regular ovulation, making it much more difficult to conceive.
This can also impact fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
A study by Ruebel, L.M. et al. found that overweight or obese women undergoing fertility treatment had abnormally high levels of fat and inflammation in the fluid surrounding their eggs, compared to women of a normal weight undergoing fertility treatment. Eggs from overweight or obese women were found to have ‘disorganized’ DNA.
How Weight Affects Fertility During Implantation
Obesity can detrimentally affect implantation in women. Studies have indicated that patients with a BMI of 30 or higher experience a decrease in implantation rates. Obese women have been observed to have impaired endometrial development which can lead to reduced implantation and live birth rates. This can be a result of the accumulation of fat in the body that triggers an inflammatory cascade. Low-grade inflammation is linked to increased rates of implantation failure. Studies have found that over 70% of females with unexplained infertility have high levels of inflammation and oxidative stress.
A study conducted between 2016-2018, included 191 IVF/ICSI cycles from non-donor eggs. Three groups were split up by BMI – normal, overweight and obese. The study found that women who were overweight or obese had significantly lower pregnancy, implantation, and live birth rates compared to those with normal weight.
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine Fibroids are non-cancerous lumps of tissue found in the uterus. According to Hopkins Medical, an estimated 20%-50% of women of reproductive age currently have fibroids and 77% will develop fibroids during their childbearing years. Fibroids usually do not cause any problems but if they are in the wrong spot, they can cause implantation failure.
A meta-analysis showed that obesity is linked to a higher risk of uterine fibroids. The study found that the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and the risk of uterine fibroids follows an inverse J-shaped pattern, indicating a clear association. According to a case-control study, increased body fat, especially abdominal visceral fat, is capable of inducing uterine fibroids. High levels of body fat resulting in hyperestrogenism are believed to be one of the main causes of uterine fibroids.

How Weight Affects Fertility with Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is commonly associated with obesity and can have a significant impact on fertility. With insulin resistance, excess body fat forms a barrier to the insulin that is trying to get through to the bloodstream to work effectively. This causes hyperinsulinemia which can lead to carbohydrate cravings, inflammation, oxidative stress and more weight gain. This excess body fat will then produce high levels of estrogen, resulting in an increasing spiral of excess insulin and fat production, followed by excess estrogen production.
A landmark study by Brothers, J.K. et al. undertaken in 2010 on mice found that the pituitary gland responds to chronically high insulin levels by stimulating a surge of hormonal changes that impair fertility. Lean mice had six times more successful pregnancies than obese mice. Obese mice with their pituitary-insulin receptors removed had five times more successful pregnancies than obese mice with intact pituitary-insulin receptors. In addition to affecting estrogen levels, insulin resistance also impacts the production of progesterone and luteinizing hormones (LH), further altering the hormonal environment of the ovaries and impacting fertility.

How Weight Affects Miscarriage
Research has shown that maternal obesity is associated with a higher risk of miscarriage, particularly in women with recurrent miscarriages. A meta-analysis conducted in 2008 found that women with a BMI ≥25 were more likely to experience miscarriage, regardless of whether conception occurred naturally or with artificial reproduction treatment. In the case of ovulation induction, the odds of miscarriage were 5 times higher in women with a higher BMI, compared to women with a normal BMI.
The mechanisms underlying the association between obesity and miscarriage risk are not well understood. In women, abnormalities in reproductive hormone profiles, poor oocyte quality and reduced responsiveness of the endometrium for fertilization have all been hypothesized to impact the rate of miscarriage.
Research suggests that losing weight may reduce the risk of miscarriage in obese women, even among those with a history of miscarriage.

Recommendations
Now, you are probably thinking, well what should I do? Studies recommend that women should try to achieve a BMI of <29 prior to trying to get pregnant and artificial reproductive treatments like IVF. This will rule out hormone disruptions caused by excess body fat. Speak to a Radically Rooted Dietitian for a full evaluation and to determine the best method of care. Depending on age, a dietitian can make a really huge difference in weight management to optimize estrogen levels prior to IVF or months of trying to get pregnant.
Although long-term weight loss is always the goal, it is much harder to achieve and even short-term weight loss has shown to make a difference in fertility. It can not only save you months of stress about becoming pregnant but it can also save thousands of dollars on IVF attempts.
Bottom Line & Suggestions
There is a clear link between overweight/obesity and fertility. Weight affects fertility. If you’re obese or overweight and thinking of having a baby, your first step should be to talk to a Radically Rooted Dietitian. We evaluate and decide the best method of care and if needed, a safe weight loss plan. Sustainable and incremental shifts in body fat can help improve the chances of ovulation naturally, and improve the response to some ovulation medications and IVF too. Individualized dietary recommendations will be developed by taking into account your specific health status, lifestyle and dietary preferences.



