How Vitamin D Impacts Fertility
According to The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the overall prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the United States was found to be 41.6%, with the highest rates observed in non-Hispanic blacks (82.1%) and Hispanics (69.2%). There is no question that rates of vitamin D deficiency for those living in the Northeast are even higher. This is a vitamin that has profound effects on not only our bones, mental health and immune system but also fertility! Vitamin D is always a vitamin that I emphasize to patients and have seen firsthand make an impact. But let’s take a look at the stats.
Vitamin D has indirect effects on egg health. While vitamin D is primarily known for its role in maintaining bone health and supporting the immune system, emerging research suggests it impacts reproductive health.

Hormonal Balance & Implantation: Vitamin D Impacts Fertility
By promoting hormone synthesis and regulating proteins involved in fertility and pregnancy, adequate Vitamin D is essential for female reproductive health.
A key function of vitamin D is to stimulate the enzyme that converts male hormones into estrogens and progesterones (female hormones). This hormone is synthesized by vitamin D, which is crucial for fertility and pregnancy.
Vitamin D may also have a significant role in fertility by acting on the ovaries and the endometrium. At the ovarian level, vitamin D has been shown to enhance ovulation. It appears to work at a cellular level by altering AMH signaling, increasing FSH sensitivity and increasing progesterone production. In a recent study of patients undergoing IVF, those with adequate vitamin D levels had a higher chance of obtaining top-quality embryos compared to those who were vitamin D deficient. Additionally, women with adequate vitamin D levels had higher implantation rates and clinical pregnancy rates than those with levels under 20 ng/ml. Previous studies suggest this correlation is the result of an effect at the endometrial level, likely mediated through local immune responses.
According to a 2009 study, Women with higher levels of vitamin D in their serum and follicular fluid (FF) are more likely to achieve clinical pregnancy (CP) following in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Various studies show that infertile women with higher vitamin D content in plasma and/or follicular fluid levels are more likely to become pregnant after assisted reproductive procedures.

Vitamin D Impact on Female Infertility
Numerous studies reveal that vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of infertility.
An interesting study of 189 infertile women in Iran proved that severe long-lasting vitamin D deficiency caused by inadequate sun exposure to the skin due to concealing dress code is likely a cause of reduced ovarian reserve.
And that is not the only interesting study that indicated a correlation between vitamin D and infertility…
Vitamin D status may be of even more significance during fertility treatments such as IVF. In a cross-sectional study conducted at an infertility unit, IVF outcomes were examined in women who were deficient in vitamin D. The results showed that the clinical pregnancy rates were much higher in women with higher vitamin D levels compared to those with lower levels. The highest chances of pregnancy observed were in women with serum levels >30 ng/mL.
Research shows women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies (ART) who have adequate levels of vitamin D had more positive pregnancy tests, an easier time getting pregnant, and higher rates of live births compared to those with lower vitamin levels.
Vitamin D Impacts Ovarian Reserve
Ovarian reserve refers to the number and quality of eggs a woman has left for reproductive potential. It has been suggested that vitamin D assists in the production of anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) (AMH), which is the measure of ovarian reserve.
While the direct impact of vitamin D on egg quality is not yet fully understood, it is known that vitamin D is involved in various cellular processes and due to its antioxidant effects, may play a role in preventing oxidative stress and DNA damage. Optimal vitamin D levels could help support healthy egg development and maturation.
This may prompt you to the question, can vitamin D supplementation improve ovarian reserves in women with already diminished ovarian reserves? In a study conducted in 2021, participants with diminished ovarian reserve were supplemented with vitamin D. The results showed that there was a statistically significant increase in serum anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) levels.
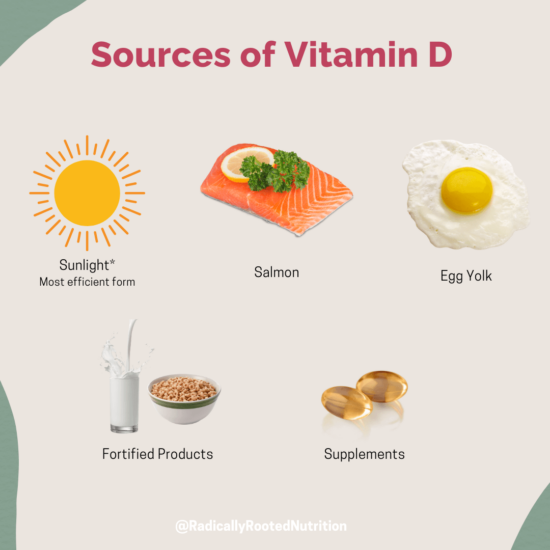
Best Sources of Vitamin D
The Institute of Medicine recommends an intake of at least 600 IU of Vitamin D3 per day with an upper limit of 1,000 IU.
Here are several ways you can boost your vitamin D levels….
- Sunlight – this is the most efficient form of vitamin D. Aim to get at least 15 minutes of direct sunlight a day.
- Seafood and Fish- these are the highest foods in vitamin D. Try incorporating salmon, tuna, oysters, and mackerel at least 2 days a week. Wild-caught fish contain higher vitamin D levels than farmed fish.
- Foods- some foods are naturally high in vitamin D or have been fortified, some examples are dairy and plant milk, orange juice, cereals, yogurts, and tofu. (Make sure to take a look at the label for vitamin D content).
Normal Vitamin D Levels & Supplementation Doses:
Sometimes sunshine and diet aren’t enough, and you may need to supplement vitamin D. This can be the case if you live somewhere that does not get very much sunlight or has a winter season. The amount you should take depends on what your vitamin D levels are.
- If your level is >45ng/ml: Supplementation is not needed.
- If your level is >30ng/ml: You should take 400-600 IU daily.
- If your level is between 20-30ng/ml (deficiency): It is recommended that you take 800-1000 IU daily (available over the counter) and recheck the level in 12 weeks.
- If your level is less than or equal to 20ng/ml (deficiency): It is recommended that you take 50,000 IU of Vitamin D once a week for 8 weeks (to be prescribed by a physician), then take 2,000 IU daily (available over the counter) and recheck level in 12 weeks.
If your level is <10ng/ml: In addition to taking 50,000 IU once a week, you will also need to be seen by an endocrinologist for long-term follow-up care.
Bottom Line
Through numerous research studies, it can be concluded that vitamin D plays a significant role in overall fertility outcomes. Though more research is needed to establish a definitive link, it is unlikely that a standard dose of Vitamin D and a little extra bit of sunlight will do any harm. If you need advice on what dose or type of vitamin D is best for you, reach out to us to schedule a 30-minute supplement consultation with a Radically Rooted Dietitian. We would love to work with you!



